How to Cover the Creation of a Processing Method for Relative Calibration - Tip124
OBJECTIVE or GOAL
Welcome back to Get Empowered! In the last Empower tip-of-the-week post for Empower Chromatography Data Software, we learned how to use the Peak Ratio functionality in the Processing Method (Tip #123).
In this week’s tip, we are going to begin a new series on how to work with GPC/SEC data in Empower.
Topics will include:
- Creating a Processing Method
- Working with different types of calibration, such as Relative, Universal, and Cumulative Matching Calibration
- Working with multiple detectors
GPC, or Gel Permeation Chromatography, is referred to when working with organic polymers. SEC, or Size Exclusion Chromatography, is referred to when working with biomolecules. In both cases this type of chromatography is the separation of compounds based on their effective size in solution.
This tip will cover the creation of a Processing Method for Relative Calibration using narrow, or monodisperse, standards. The advantages to this technique are that it is easy and accurate for polymers of the same chemical nature as the standards. The disadvantage is that narrow standards are not available for every type of polymer.
ENVIRONMENT
- Empower
PROCEDURE
- Select representative chromatograms for standards and samples and bring them into Review. Typically, relative calibration with narrow standards is done by injecting mixtures, or cocktails, of monodisperse standards. Start by adding the molecular weights into the Component Editor for each of the standard vials either in Run Samples or Alter Sample.
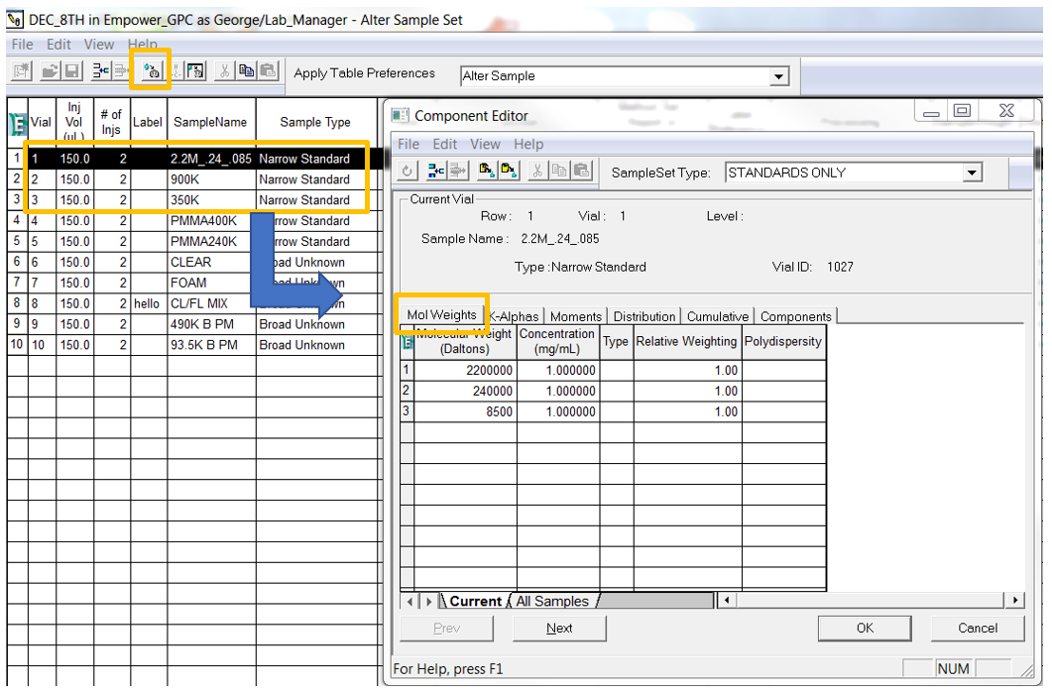
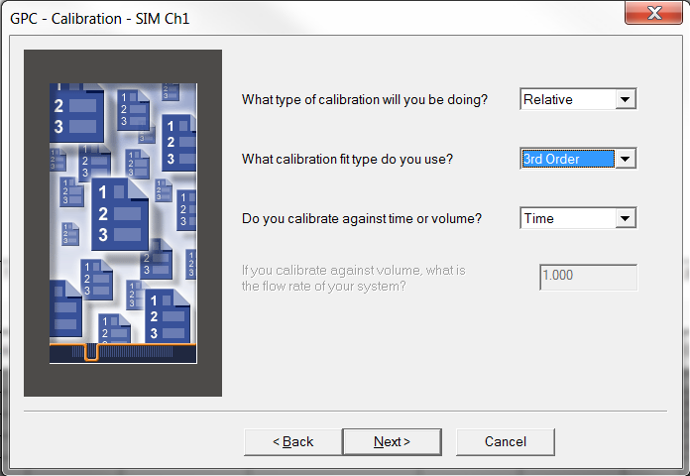
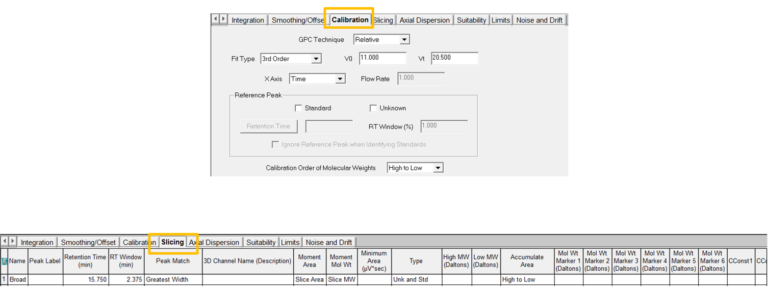
- Create a new Processing Method with the wizard if you are new to working with GPC data. Most of the screens will be like developing a Processing Method when working with LC data with a couple of differences. The Calibration window requires you to select the type of calibration, the calibration fit and x-axis for the calibration curve. If it is determined that the fit needs to be modified after a calibration curve has been generated, that can be done and will be discussed in the next tip.
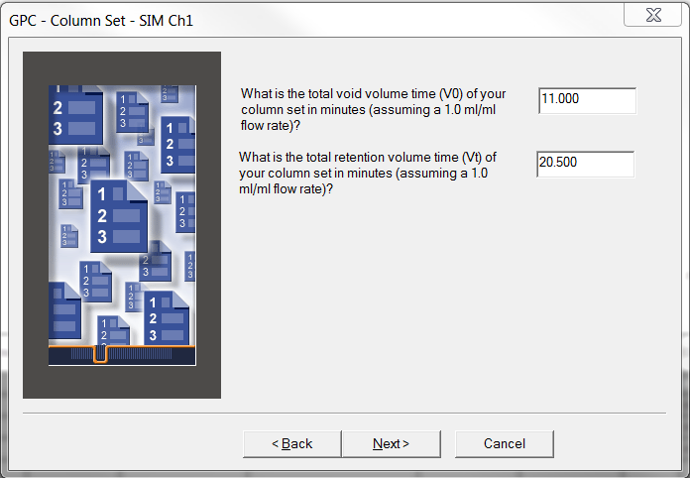
- The Column Set window requires a void volume time, or exclusion limit and a total volume time, or permeation limit. These values will depend on the column or column bank being used.
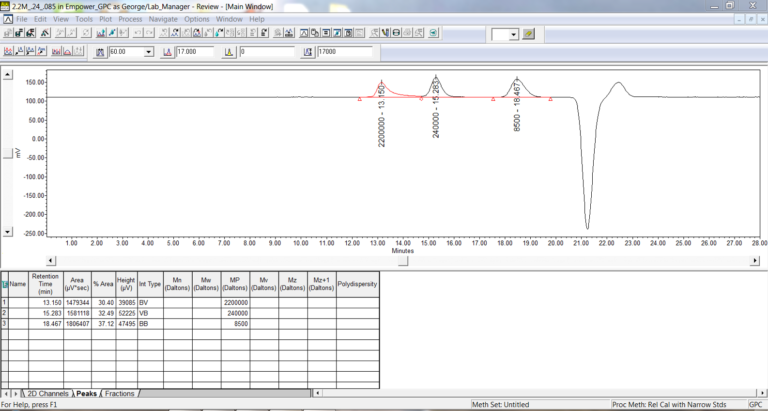
- Once you finish going thru the wizard, check the integration for the standards and modify as needed so that only the peaks for the monodisperse standards are integrated.
- Select a sample and then click the Processing Method Wizard tool to modify the Processing Method for broad samples. When the Wizard opens, click the Back button a few times to get to the peak detection and integration parameters and then proceed thru the wizard.
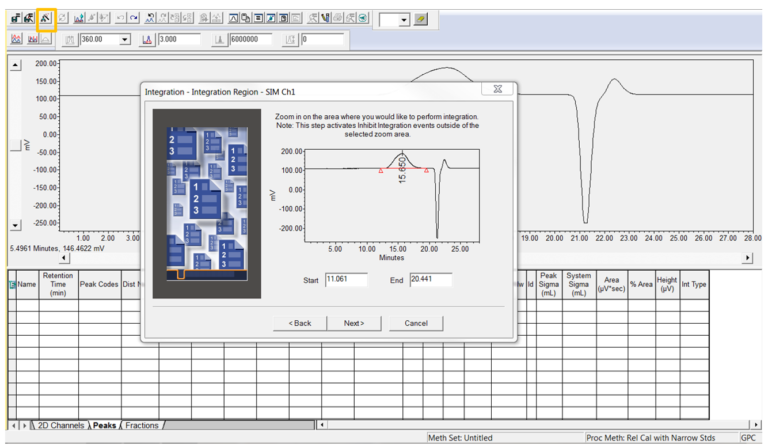
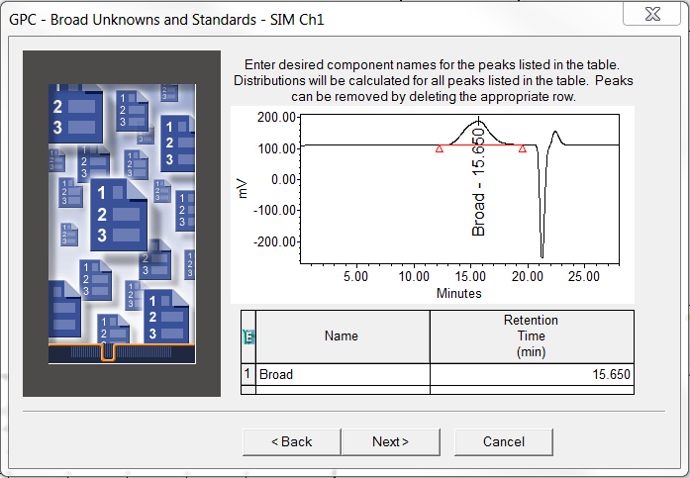
- On the Broad Unknowns and Standards window you can enter a name for the broad sample.
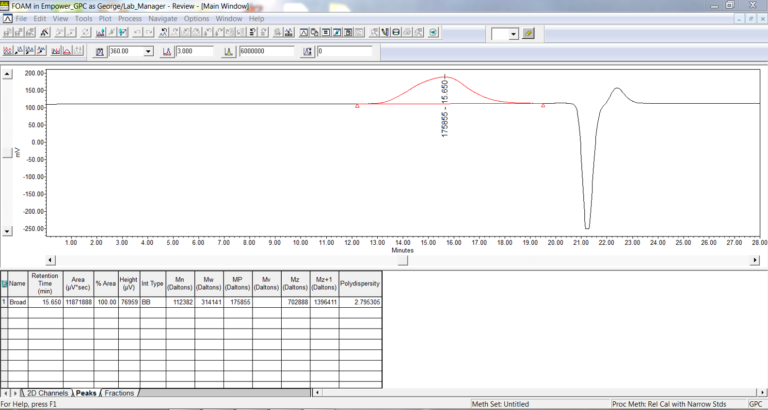
- Save all the changes to the Processing Method and exit out. Check the integration on the chromatograms for the broad samples and modify as needed.
-
Alternatively, you could develop a Processing Method without the wizard. For peak detection and integration, the Integration tab has parameters for both narrow and broad peaks.
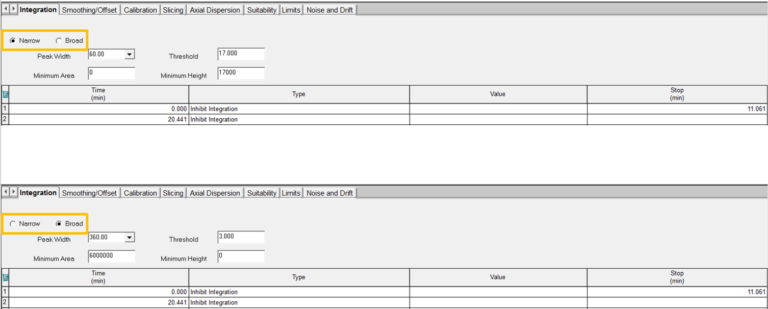
- In addition, go to the Calibration tab to set the calibration parameters including V0 and Vt. Finally, the Slicing tab allows you to name the broad sample.
It’s that easy!
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION
id67989, EMP2LIC, EMP2OPT, EMP2SW, EMP3GC, EMP3LIC, EMP3OPT, EMP3SW, EMPGC, EMPGPC, EMPLIC, EMPOWER2, EMPOWER3, EMPSW, SUP

