What's the difference between the various fasta format options in Progenesis QI for Proteomics and PLGS? - WKB201722
ENVIRONMENT
- ProteinLynx Global Server (PLGS)
- Progenesis QI for Proteomics
ANSWER
In the New Databank and Edit Databank options menu in PLGS, you are asked to choose a Fasta format from a list of options.
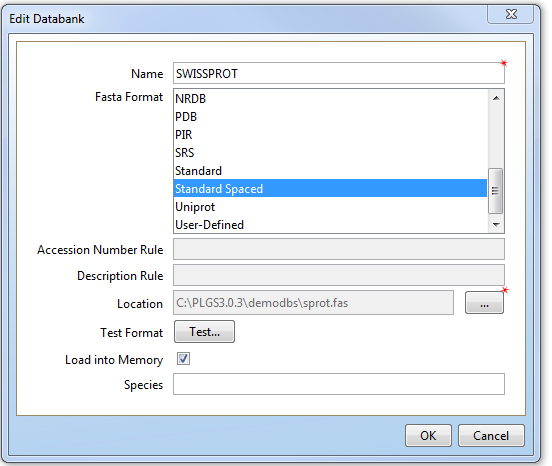
Similarly, in the Identify Peptides tab of Progenesis QI for Proteomics, you are asked to select both a fasta file and the format of that fasta file.
So what's the difference between these options, and why are there several options for what's supposed to be a standard amino acid sequence library file format?
All the options follow the basic fasta format; the difference is how they arrange the data in the header of each sequence within the fasta file. FASTA format consists of a description line, beginning with a “>” symbol, followed by multiple lines containing the sequence of amino acid characters in 60-character blocks. What follows the the ">" symbol and what precedes the sequence can vary in both content and order of content. Many of them use the pipe symbol "|", colons, or semi-colons to separate fields. PLGS and Progenesis QI for Proteomics both need to know which version of fasta format is being used so they can correctly read the information about each identification from the header and display it in the results. If you select a fasta variant that's not correct for the fasta file your using, the results may look a bit odd. The PLGS3.0.3 library import/editor tool has a test button that you can use to confirm that you've selected the right fasta variant when importing a fasta file into the sequence library.
Descriptions of some commonly used fasta variants:
FASTA STANDARD
Description line: >NAME|ACCESSION_NUMBER|DATABANK_OF_ORIGIN: DESCRIPTION
Example:
>IF3_AQUAE|O67653|SPT: Translation initiation factor IF-3.
MSKLKEYRVNRQIRAKECRLIDENGQQIGIVPIEEALKIAEEKGLDLVEIAPQAKPPVCK
IMDYGKFKYELKKKEREARKKQREHQIEVKDIRMKVRIDEHDLQVKLKHMREFLEEGDKV
KVWLRFRGRENIYPELGKKLAERIINELSDIAEVEVQPKKEGNFMIFVLAPKRKK
FASTA NCBI_EXPASY_STANDARD
This format comes in two different forms: a 2-pipe version, and the 4-pipe version shown below. The description line of this particular data bank format is not shortened in any way. The Fasta NCBI EXPASY standard option in PLGS and PQIP accepts both 2- and 4-pipe versions.
Description line (2 pipes): >NAME|ACCESSION_NUMBER|DATABANK_OF_ORIGIN: DESCRIPTION
Description line (4 pipes): >gi|NUMBER|DATABANK_OF_ORIGIN|ACCESSION_NUMBER|LOCUS_OR_NAME DESCRIPTION
Example of 2-pipe version:
>SP|PLASM_FALCI|(P08978) metal binding protein (DHHC domain) [Plasmodium falciparum 3D7]
MIIWCHIKCLCTNPGFLNETFHFVSDNTTEYDNNVQMCKKCNLLKIKRSHHCSVCDKCIMKMDHHCFWIN
SCVGLYNQKYFILLNFVRTKGKYNTNIIKHL
Example of 4-pipe version:
>gi|3845261|gb|AAC71934.1| metal binding protein (DHHC domain) [Plasmodium falciparum 3D7]
MIIWCHIKCLCTNPGFLNETFHFVSDNTTEYDNNVQMCKKCNLLKIKRSHHCSVCDKCIMKMDHHCFWIN
SCVGLYNQKYFILLNFVRTKGKYNTNIIKHL
FASTA STANDARD_SPACED
No pipes in the sequence headers. Description line: >NAME ACCESSION_NUMBER DESCRIPTION
Example:
>IF3_AQUAE (O67653) Translation initiation factor IF-3.
MSKLKEYRVNRQIRAKECRLIDENGQQIGIVPIEEALKIAEEKGLDLVEIAPQAKPPVCK
IMDYGKFKYELKKKEREARKKQREHQIEVKDIRMKVRIDEHDLQVKLKHMREFLEEGDKV
KVWLRFRGRENIYPELGKKLAERIINELSDIAEVEVQPKKEGNFMIFVLAPKRKK
FASTA Uniprot
A sample Uniprot entry is shown below. In this example, one accession number (Q4U9M9) is followed by a pipe symbol "|", and then the entry name (104K_THEAN) and description
>Q4U9M9|104K_THEAN 104 kDamicroneme-rhoptry antigen precursor (p104) - Theileriaannulata
MKFLVLLFNILCLFPILGADELVMSPIPTTDVQPKVTFDINSEVSSGPLYLNPVEMAGVK
YLQLQRQPGVQVHKVVEGDIVIWENEEMPLYTCAIVTQNEVPYMAYVELLEDPDLIFFLK
EGDQWAPIPEDQYLARLQQLRQQIHTESFFSLNLSFQHENYKYEMVSSFQHSIKMVVFTP
KNGHICKMVYDKNIRIFKALYNEYVTSVIGFFRGLKLLLLNIFVIDDRGMIGNKYFQLLD
DKYAPISVQGYVATIPKLKDFAEPYHPIILDISDIDYVNFYLGDATYHDPGFKIVPKTPQ
CITKVVDGNEVIYESSNPSVECVYKVTYYDKKNESMLRLDLNHSPPSYTSYYAKREGVWV
TSTYIDLEEKIEELQDHRSTELDVMFMSDKDLNVVPLTNGNLEYFMVTPKPHRDIIIVFD
GSEVLWYYEGLENHLVCTWIYVTEGAPRLVHLRVKDRIPQNTDIYMVKFGEYWVRISKTQ
YTQEIKKLIKKSKKKLPSIEEEDSDKHGGPPKGPEPPTGPGHSSSESKEHEDSKESKEPK
EHGSPKETKEGEVTKKPGPAKEHKPSKIPVYTKRPEFPKKSKSPKRPESPKSPKRPVSPQ
RPVSPKSPKRPESLDIPKSPKRPESPKSPKRPVSPQRPVSPRRPESPKSPKSPKSPKSPK
VPFDPKFKEKLYDSYLDKAAKTKETVTLPPVLPTDESFTHTPIGEPTAEQPDDIEPIEES
VFIKETGILTEEVKTEDIHSETGEPEEPKRPDSPTKHSPKPTGTHPSMPKKRRRSDGLAL
STTDLESEAGRILRDPTGKIVTMKRSKSFDDLTTVREKEHMGAEIRKIVVDDDGTEADDE
DTHPSKEKHLSTVRRRRPRPKKSSKSSKPRKPDSAFVPSIIFIFLVSLIVGIL
FASTA LONG_DESCRIPTION
Description line: >NAME DESCRIPTION
This format is used when the description is very long. In the ProteinLynx display, the description is truncated to fit into the viewing area.
Example:
>gp:AL034396_1 PID:5441319 Human DNA sequence from clone 1158B12 on chromosome Xp11.21-11.4 Contains the ZXDA gene for X-linked duplicated Zinc finger A, and MYCL1 (v-myc avian myelocytomatosis viral oncogenehomolog 1, lung carcinoma derived) and KRT8 (Keratin 8, Cytokeratin 8, CYK8, Keratin type II skeletal 8) pseudogenes. Contains ESTs, an STS, GSSs and a CpG island, complete sequence; match: proteins: Sw:P98168 Sw:P98169. (gb:AL034396)
MEIPKLLPARGTLQGGGGGGIPAGGGRVHRGPDSPAGQVPTRRLLLPRGPQDGGPGRRRE
EASTASRGPGPSLFAPRPHQPSGGGDDFFLVLLDPVGGDVETAGSGQAAGPVLREEAKAG
PGLQGDESGANPAGCSAQGPHCLSAVPTPAPISAPGPAAAFAGTVTIHNQDLLLRFENGV
LTLATPPPHAWEPGAAPAQQPRCLIAPQAGFPQAAHPGDCPELRSDLLLAEPAEPAPAPA
PQEEAEGLAAALGPRGLLGSGPGVVLYLCPEALCGQTFAKKHQLKMHLLTHSSSQGQRPF
KCPLGGCGWTFTTSYKLKRHLQSHDKLRPFGCPAEGCGKSFTTVYNLKAHMKGHEQENSF
KCEVCEESFPTQAKLGAHQRSHFEPERPYQCAFSGCKKTFITVSALFSHNRAHFREQELF
SCSFPGCSKQYDKACRLKIHLRSHTGERPFLCDFDGCGWNFTSMSKLLRHKRKHDDDRRF
MCPVEGCGKSFTRAEHLKGHSITHLGTKPFVCPVAGCCARFSARSSLYIHSKKHLQDVDT
WKSRCPISSCNKLFTSKHSMKTHMVKRHKVGQDLLAQLEAANSLTPSSELTSQRQNDLSD
AEIVSLFSDVPDSTSAALLDTALVNSGILTIDVASVSSTLAGHLPANNNNSVGQAVDPPS
LMATSDPPQSLDTSLFFGTAATGFQQSSLNMDEVSSVSVGPLGSLDSLAMKNSSPEPQAL
TPSSKLTVDTDTLTPSSTLCENSVSELLTPAKAEWSVHPNSDFFGQEGETQFGFPNAAGN
HGSQKERNLITVTGSSFLV
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION
id201722, isopropanol, SUPPLGS

