Helpful Empower Tools: Using Relative Retention Time to Identify Peaks - Tip339
OBJECTIVE or GOAL
Use relative retention time, rather than absolute retention times, to identify peaks if the variation in retention time becomes excessive.
ENVIRONMENT
- Empower
- Empower Tip of the Week #339
PROCEDURE
STEP 1
Start with a standard containing four properly identified components (Figure 1).

STEP 2
In the sample chromatogram, peak #3 has shifted and is not identified. The peak type is Unknown. The peak table also shows that peak #3 is missing. Notice the peak at 8.033 minutes, which Empower has not identified (Figure 2).

STEP 3
Select a Retention Time Reference peak from the RT Reference field on the Components tab of the Processing Method (Figure 3).

STEP 4
Working with the chromatogram for the standard, click Calibrate and unhide RRT~ in the Peaks table. RRT~ is calculated as RT of Peak of interest/RT of RT Reference peak (Figure 4).

STEP 5:
Make the following modifications on the Components tab of the Processing Method (Figure 5):
- Remove the retention time for the peak.
- Specify the RRT value in the field for the peak.

STEP 6
This is the calculation for the temporary retention time used for peak identification. This does not change anything on the Components tab of the Processing Method. Substituting in the real numbers: 1.666 x 4.842 = 8.067 +/- 0.091 (Figure 6).
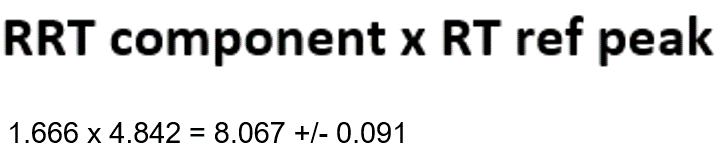
STEP 7
The temporary expected retention time for the peak is 8.067 +/- 0.091 minutes. The peak at 8.033 minutes now falls within the new retention time window and is identified properly (Figure 7).

ADDITIONAL INFORMATION
This can be done via the Pro or QuickStart interface.

