How do AccQ•Fluor and AccQ•Tag Ultra reagents derivatize amino acids? - WKB238328
ENVIRONMENT
- AccQ•Fluor
- AccQ•Tag
- Amino acid analysis (AAA)
- Derivatization
ANSWER
AccQ•Fluor and AccQ.Tag Ultra reagents derivatize amino acids in the same way because both reagent kits contain the same components.
The AccQ•Tag Ultra method is based on a derivatizing reagent developed specifically for amino acid analysis. Waters AccQ•Tag Ultra reagent (6-aminoquinolyl-N-hydroxysuccinimidyl carbamate, or AQC) is an N-hydroxysuccinimide-activated heterocyclic carbamate (a class of amine-derivatizing compounds).
Figure 1–1: Waters AccQ•Tag Ultra reagent

Reagent chemistry:
The AccQ•Tag Ultra reagent converts both primary and secondary amino acids to stable derivatives, as illustrated in the following figure. The structure of the derivatizing group is identical for all amino acids, adding both UV absorbance and fluorescent character. Excess reagent hydrolyzes to yield 6-aminoquinoline (AMQ), a non-interfering by-product. Note: The derivatization peak is labeled in the chromatogram and always appears. Its size and amount varies from batch to batch and changes over time. Because of that variance, the peak’s size is not quantitatively or diagnostically significant.
Figure 1–2: AccQ•Tag Ultra reaction:

Reaction with amino acids:
The AccQ•Tag Ultra reagent reacts rapidly with primary and secondary amino acids to yield highly stable ureas. The resulting derivatives are stable at room temperature for as long as one week, provided that you prevent evaporation of the sample solvent.
Reagent hydrolysis:
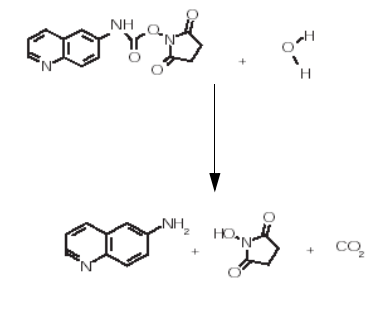
In a slower reaction, excess reagent hydrolyzes to produce 6-aminoquinoline (AMQ), N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS), and carbon dioxide (see the following figure). The destruction of excess reagent occurs within one minute. The major hydrolysis product, AMQ, produces a significant peak that is easily resolved chromatographically. NHS and carbon dioxide do not interfere with the analysis.
Figure 1–3: AccQ•Tag Ultra reaction in the presence of water
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION
A derivatization peak (AMQ) is always present in all AccQ•Tag chromatography and must be separated from the labeled amino acids.
The traditional AccQ-Tag for HPLC method uses a Fluorescence detector with the associated HPLC AccQ-Tag eluents, so the peak height of the AMQ is low due to the response under Fluorescence conditions.
The AccQ-Tag derivatization peak (AMQ) produces a strong response with UV, and is visible in both the HPLC and AccQ•Tag Ultra methods on ACQUITY UPLC systems.
Related information:
AccQ•Fluor Reagent Kit Care & Use Manual (lit code wat0052881)
AccQ•Tag Ultra Derivatization Kit Care & Use Manual (lit code 715001331)
id238328, 2695UP

